3D Plotter
-
Home
-
3D Plotter
3D Plotter
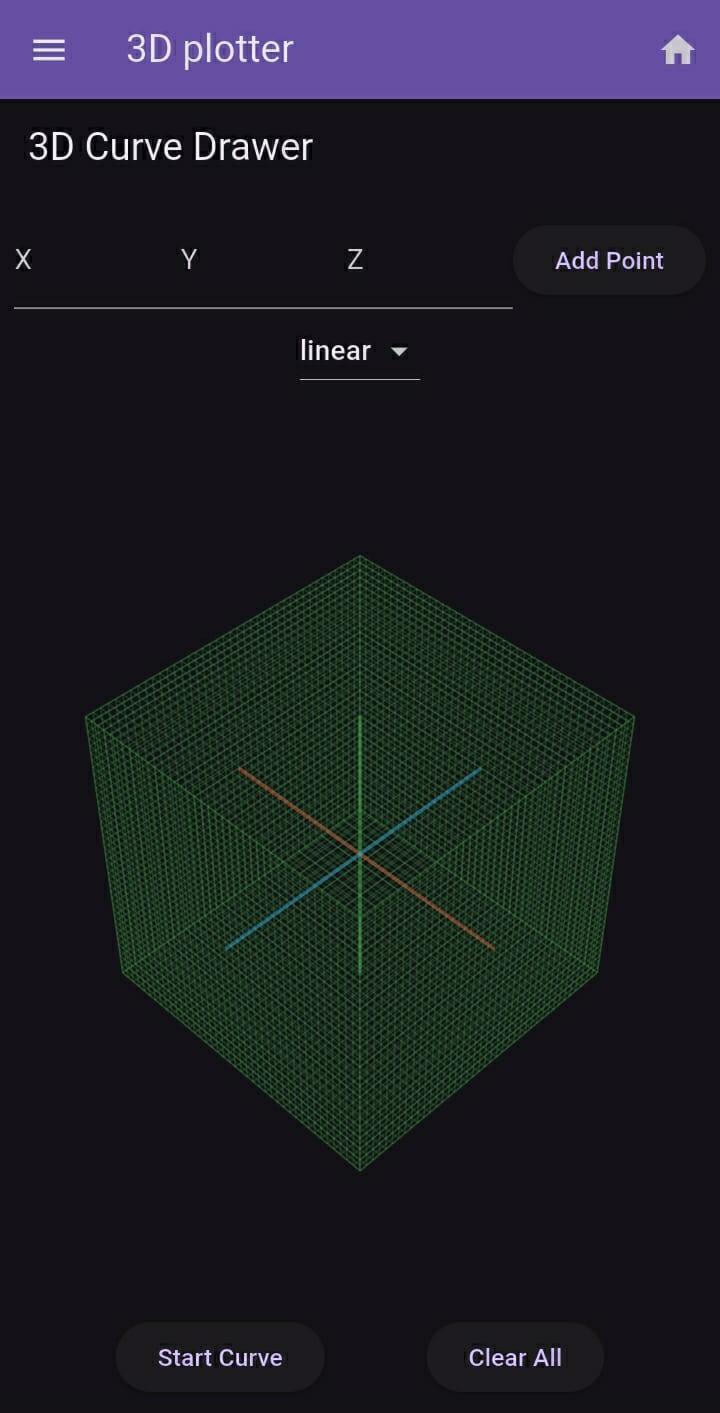
The Future of Design and AI: Exploring Higher Dimensions with 3D Curve Drawing
A New Dimension of Creative Expression
This advanced 3D curve drawing application represents far more than a simple visualization tool—it's a gateway to understanding how higher-dimensional thinking will revolutionize design and artificial intelligence. By enabling the creation of complex 3D curves through mathematical interpolation, this technology bridges the gap between abstract mathematical concepts and tangible spatial representations.
The Technical Foundation
The application implements three powerful curve-generation algorithms:
Linear Interpolation: The simplest connection between points in 3D space, forming the basis for more complex curves
Bézier Curves: Using Bernstein polynomials to create smooth curves defined by control points
Catmull-Rom Splines: Creating C1 continuous curves that pass through all control points
These mathematical constructs don't just draw lines—they encode fundamental principles of spatial relationships that mirror natural phenomena from DNA helices to galactic arms.
Impact on Future Design Paradigms
1. Generative Design Revolution
AI-Assisted Creation: The curve algorithms can serve as building blocks for generative AI systems that create complex 3D structures
Parametric Modeling: Designers will manipulate higher-level parameters while AI handles the mathematical complexities
4D Design Tools: Adding temporal dimensions to create animated, morphing structures
2. Manufacturing Transformation
3D Printing Optimization: Complex curves enable lightweight, structurally efficient designs impossible with traditional CAD
Nanoscale Fabrication: Precise mathematical curves guide molecular assembly in advanced materials
Robotic Construction: Continuous curves replace segmented paths for smoother robotic motions
3. Architectural Innovation
Organic Structures: Free-form curves inspired by natural forms
Structural Integrity: Mathematical optimization of curved load-bearing elements
Dynamic Buildings: Shape-shifting structures following parametric curves
AI Implications and Developments
1. Spatial Intelligence Enhancement
3D Pattern Recognition: Training AI to understand complex spatial relationships
Curve Prediction: AI suggesting optimal curve paths based on design intent
Dimensional Reduction: Converting high-D data into 3D visualizations
2. Machine Learning Applications
Physics Simulation: AI predicting how curved structures will behave under stress
Material Science: Discovering new materials based on molecular curve patterns
Biological Modeling: Simulating protein folding and DNA structures
3. Human-AI Collaboration
Creative Partnership: Humans define artistic intent while AI handles mathematical optimization
Educational Tools: Interactive learning of complex mathematical concepts
Design Democratization: Making advanced 3D modeling accessible to non-experts
The Higher-Dimensional Future
This technology points toward several groundbreaking developments:
4D Design Interfaces: Incorporating time as a fourth dimension in modeling
Quantum Curves: Representing probability clouds in quantum system visualizations
Topological AI: Machines that understand and manipulate complex spatial relationships
Neural Geometry: Brain-inspired network structures based on 3D curve optimization
As we stand at the precipice of this new era, tools like this 3D curve drawer serve as both practical instruments and conceptual bridges—helping designers, engineers, and AI systems alike to think beyond flat sketches and rigid models, into a world where form follows mathematical beauty, and complexity emerges from simple, elegant curves.
The future of design isn't just about what we can imagine—it's about what we can mathematically describe and visually represent in multidimensional space. This application provides a glimpse into that future, where the boundaries between mathematics, design, and artificial intelligence blur into a new creative continuum.
Share this service: